We have been made aware of unauthorized use of our company name in fraudulent activities. Fleava only operates through fleava.com. Any other domains or contacts claiming to represent us are fraudulent.
If you receive suspicious messages, do not engage—report them to the authorities. For official inquiries, contact hello@fleava.com.
UI + UX: Two Different but Complimenting Practices
/ Journal — Insight: User Experience
Many companies are now running their companies digitally. We rarely see someone running a company without a digital component. A strong User Interface (UI) is very important for business owners because it makes a good impression on users, especially new users, tend to be more interested in the appearance of the product when they are still choosing the platform over the features themselves.
However, once they run the feature, users want fast access, transaction optimization and a seamless experience with all the basic needs across all platforms, and this is where user experience (UX) matters.
Each UI/UX designer has their own thoughts and viewpoints while building a product, but in the end, the user is the one who determines if the designs are successful or not. The ability to apply targeted tactics across the market and its digital ecosystem are therefore provided to businesses by the UI/UX designer who has a strong understanding of user behavior and habits.
User Interface
"User Interface" stands for "UI" in UI design. The application's graphical user interface is the presentation. The essence of the user interface is human-computer contact and communication in a device. It's like the User Interface is the first impression that the user gets when running the system.
In other words, the user interface is a visual design display that represents a system that users can see. It also refers to the way users engage with a website or app. Many companies are now placing greater emphasis on UI in an effort to improve user experience as a result of the increasing reliance of many businesses on web and mobile apps.

Tesla’s User Interface.
Why UI Matters
In order to fulfill user expectations and promote your site's efficient operation, the user interface is crucial. In contrast, with a simple design, and responsiveness, a well-done user interface facilitates efficient interaction between the user and the program, app, or machine. Here are some explanations for you why UI matters:
1. It aids in defining your Brand's vision
Your brand concept and UI design are focused on your customers. You can improve your UI as well as become more aware of who you are as a brand and what you want to give your people by observing their behaviors and preferences. This not only provides your branding efforts focus but also gives you a significant competitive advantage.
2. Anticipates and meets customer expectations
When the UI design has been adequately and thoroughly informed by user research, it can predict the next action a user may want to do. As a result, it has attributes, capabilities, and components that meet up to those expectations.
3. Seamless experience
Not all UI is effective UI. A good user interface design anticipates user needs and adapts to them. It becomes intuitive as a result of learning from user behavior. A strong user-interface design must incorporate all three of its essential elements—visual design, interactive design, and information architecture—to attain such sophistication. When done correctly, it significantly improves the user experience and transforms into something practical and natural in its capacity to facilitate users' task completion.
A good user interface design anticipates user needs and adapts to them.
4. Makes navigation enjoyable to use
A user interface is functional when it is easy to use, includes familiar parts and features, and doesn't require any training to utilize. Navigation of the site is made enjoyable when the UI is created using these ideas. Everything on the website should be easily accessible within three clicks or fewer because of the clear labeling of the elements and the absence of hidden menu and page links.
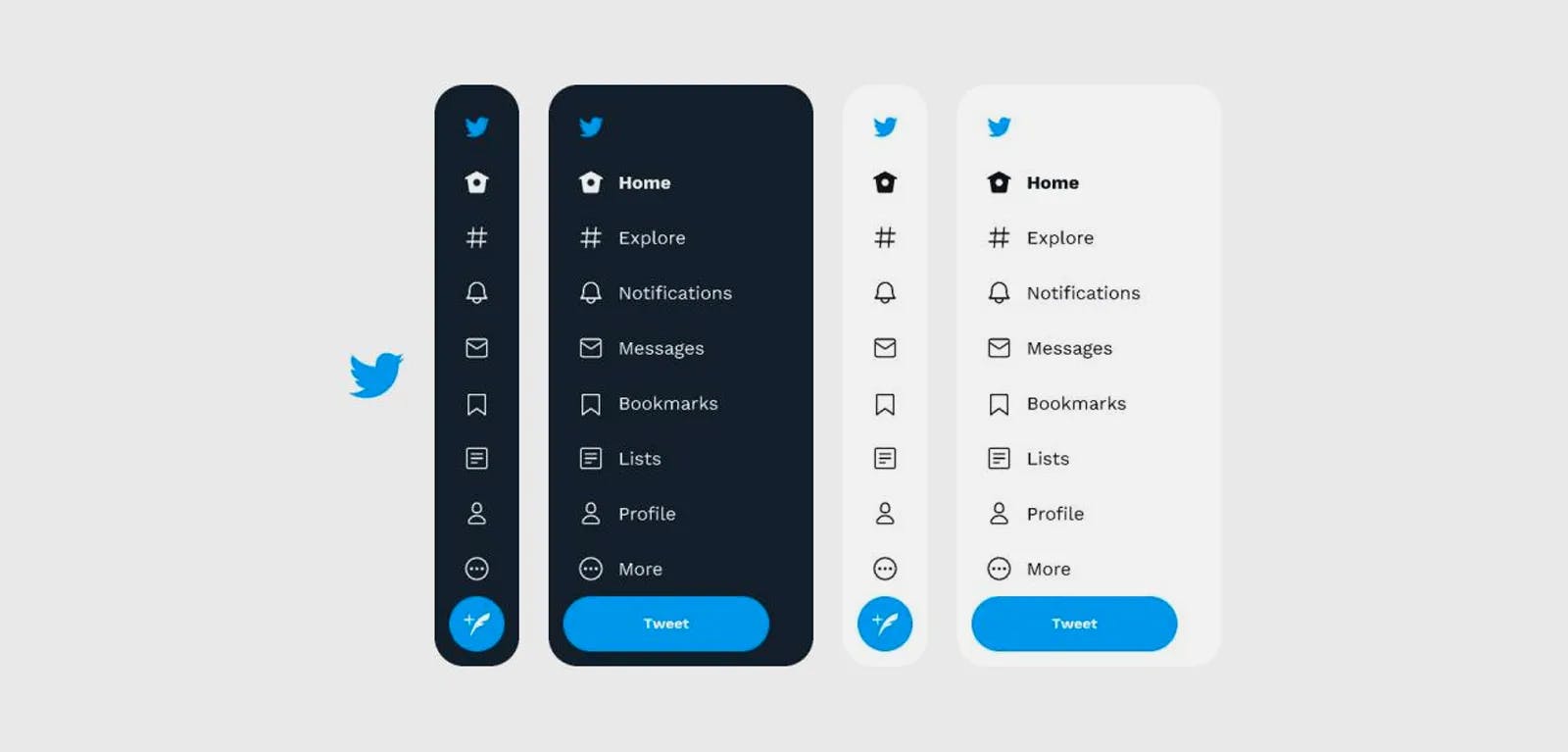
Twitter’s Navigation UI.
5. Improve Customer Satisfaction
Simple, usability-focused web user interfaces significantly improve the UX component of the process. It raises customer happiness and guarantees that every time a user visits, they are able to successfully complete their intended task. Returning to a website will become more appealing if it is user-friendly and attractive.
UI is functional when it is easy to use, includes familiar parts and features, and doesn't require any training to utilize.
In the end, we may characterize it as a quick imitation of an original idea or product that can be used as a tool to attract funding investment, improve your crowdfunding campaign, or just kick off the design process. Once created, they can be improved upon or changed to meet the needs of the audience or to enhance functionality.
User Experience
Every interaction that a person has with a product or service is referred to as User Experience or UX. Every component that affects this experience is taken into account in the UX design, as well as how users feel and how simple it is for them to complete the desired activity. This can include everything from how tangible items feel in your hand to how simple the internet checkout process is.
The responsibility of a UX Designer is to ensure that step by step goes logically and clearly, and understands user's needs. UX Design strives to provide a simple, effective, relevant and enjoyable experience for users.
To create seamless user experiences for products, services, and processes, UX designers combine market research, product development, strategy, and design. They create a connection with the client, enabling the business to better comprehend—and meet—their wants and expectations.
Why does UX matter?
User Experience is essential because it works to meet the demands of the user. It seeks to deliver satisfying experiences that maintain a user's loyalty to the good or service. A meaningful user experience also enables you to specify consumer journeys on your product that are most beneficial to commercial achievement.
UX seeks to deliver satisfying experiences that maintain a user's loyalty to the good or service.
- UX aims to meet user needs and improve the satisfaction-conversion-retention cycle for customers.
- UX attempts to give users satisfying experiences that encourage brand or product loyalty.
- UX develops a two-way relationship between the product's creator and the consumer and defines the customer journeys on your product.
- UX lowers development, bug-fixing, marketing, and other costs.
- UX increases return on investment (ROI).
Read: UX is the new SEO
User Experience Strategy
1. Define business strategy through Stakeholder interview
Engage the decision-makers and business executives early on in your project. You should not be focused entirely on the user as a UX designer—now is the time to concentrate more on the business aspect.
What market position does the product you're designing have? What are the broad aims and objectives of the company? How do stakeholders evaluate the product's performance? By responding to these inquiries up front, you can be confident that your focus will always be on the brand and company before shifting to the user.
2. Determine differentiation strategies using Competitive Research and Analysis
You can start evaluating where the product stands in the competitive landscape once you understand how to integrate your design with the corporate brand and strategy. To entice a user to begin using your product, you must first provide value. Where is the source of that value? What sets you apart from the competition?
Look at what is presently available on the market to meet this customer demand, and consider the important elements that will make your design stand out from the competition.
3. Keep the User in mind and validate User Research
Make sure that you are creating a product that consumers will genuinely love to use. Obtain early feedback from your target audience to achieve this. Surveys and questionnaires, focus groups, A/B testing, card sorting, interviews, and field studies are a few methods you might use to approach this.
Take the value you anticipate your product will provide and test it with actual customers. Consider taking a step back and rethinking your offering if the data does not support the value you have anticipated.
4. Establish clear design objectives to reach your goal
Knowing where you are now and where you want to go are both crucial. Define some precise metrics to measure the success of your design using the information you've gathered from users and stakeholders. Be clear about your goals, your approach to achieving them, and how you'll know if and when you've succeeded.
5. Conduct structured experiments and improve the findings
A desire to try new things and fail often goes into creating the perfect product that users adore. Let your UX strategy direct your efforts as you develop your design. As you develop, keep verifying the strategy and your design. Make a minimum viable product (MVP), test it with actual consumers, and then iterate on it in response to their suggestions.
How to develop your User Experience design
Following these user experience design best practices can help you increase user engagement and hit your conversion targets.
1. Understand
Ideally, you will be aware of your visitors' needs before they express them. This is accomplished by developing fully developed buyer personas that include their demographics and the difficulties they encounter. You can be trying to convert different buyer personas for your business. In such a situation, buyer persona profiles for each sort of prospect should be established, complete with information about their positions, aims, goals, difficulties, and whatever else you can learn about them.
2. Research
Don't presume you are an expert on your clients. Investigate and carry out polls. Simply listening to your prospects' conversations on social media will help you conduct your due diligence. What needs are they expressing? Which obstacles are they attempting to overcome? You may improve your UX design and achieve even better results by paying attention to these crucial factors.
3. Wireframe
When building a website or app, there are several aspects to consider, including Brand Manuals, screen and device sizes, and UI/UX trends. Wireframes provide the designer with a roadmap for preset functionality and content that is intended to accomplish a specified purpose, which can save time and money.
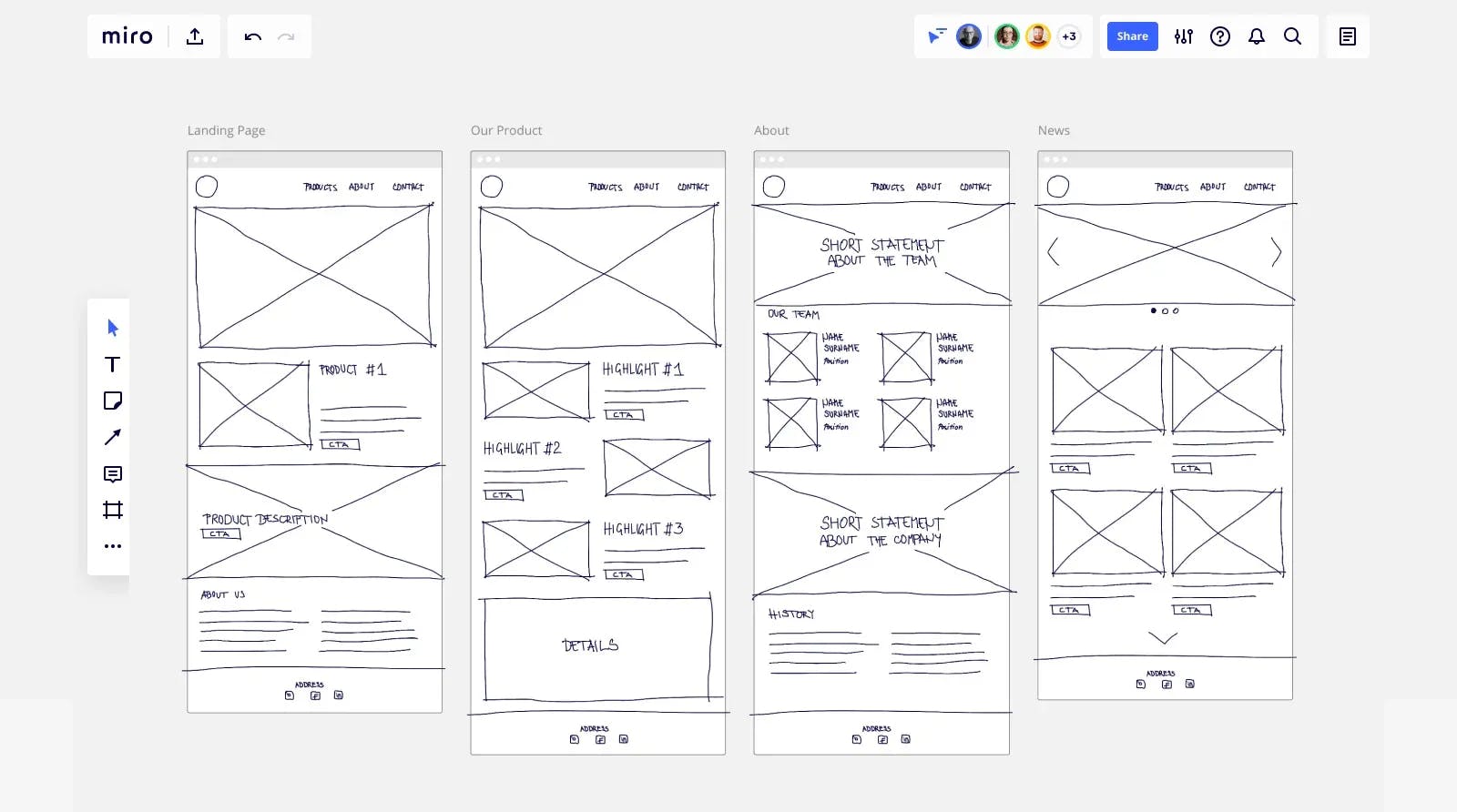
Wireframe example.
This step also includes testing and evaluating the wireframes. The design team creates the first sketches and presents them to stakeholders for feedback. It's critical to remain focused on your objective throughout the process: creating a useful design that will satisfy the end user.
Wireframes are streamlined visual schematics that show the basic structure of a website. They were typically given in black and white before design and did not specify a visual aesthetic, typography, or artwork. Wireframes outline the pages and forms of functionality, videos, image galleries, navigation, etc., that are necessary to help your website accomplish its objectives.
4. Design
After we have all the wireframes and a clear overview of the user flow and what will be featured on each screen, we now start the Mockup Design process. Designers need to have a thorough awareness of the goals, problems and difficulties of their target audience so that UX designers can create user-centric designs. This can be achieved by research that has been done previously.
When carrying out the design process, the UX designer should pay attention to the following factors:
- Information architecture (IA) is the process of organizing information and data in a way that enhances user intuition in navigation
- Style guideline is a document that details the decisions and standards made inside the organization in order to maintain alignment between the design and development teams. Being linked to the manual design enables a specific prototype to be developed more quickly and without issues.
- Visual design elements such as image layouts, ornaments, or symbols that facilitate user interaction with the interface are tested by the UX designer using wireframes and prototypes.
- Low-fidelity prototypes is a quick and simple method for turning high-level design concepts into observable and testable artifacts. Lo-fi prototypes' primary and most crucial job is to test and verify functioning, not the product's aesthetic appeal.
- Usability refers to how easily a product can be utilized by its intended users to achieve its goals. The product's learnability, efficiency, recall, error rate, and user satisfaction are the five main components.
- Accessibility is the extent to which a product can be used, understood, and accessible to people with disabilities. This could require, for example, creating a sound interface for the visually impaired or allowing larger fonts or element sizes for older people.
5. High-Fidelity Prototype
High-fidelity Prototype is a simulation or sample version of a finished product, which UX teams utilize for testing prior to launch. High-fidelity (hi-fi) prototype resemble the final product as closely as feasible in appearance and functionality. Teams typically develop high-fidelity prototypes when they have a clear idea of the product they intend to develop and need to either test it with actual users or obtain stakeholder agreement for the final design before launch.
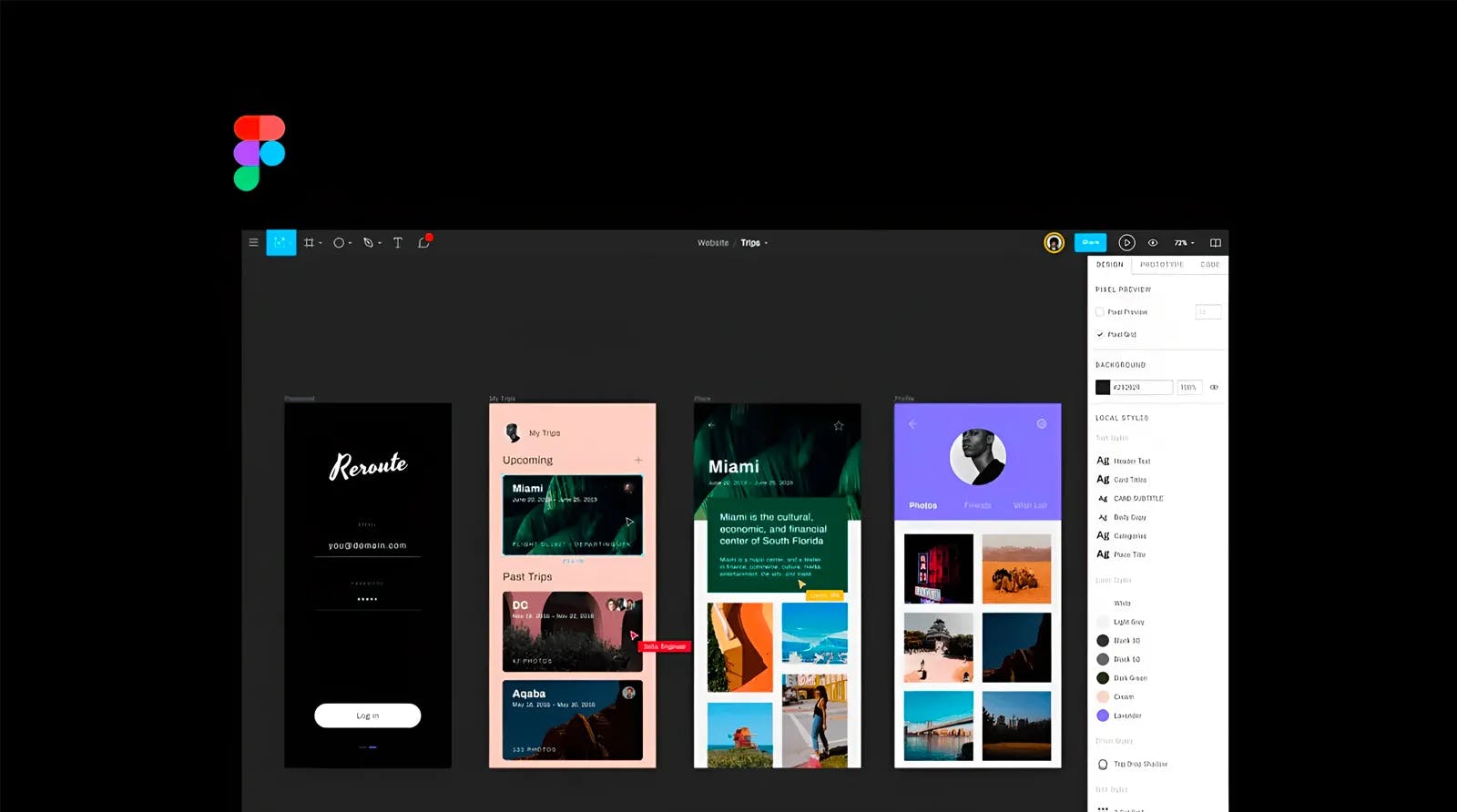
Figma, a UI/UX prototyping tool.
6. Implementation
The project enters build and launch phase whenever the team or UX designer is certain that the suggested solution will satisfy users and improve the intended business metrics. To guarantee that the design intent is carried through to the finished product, the UX designer may produce assets for the development team (or collaborate with a visual designer to do so). They may also be involved during the implementation phase.
For UX designers, it's crucial that they are successfully resolving the issues that their teams and clients are asking them to. There will always be some combination of ideation, testing, building, and measurement to do this.
7. Evaluation
You'll have a better understanding of user experience and satisfaction if you've acquired enough information about your visitors' interactions. When it comes to UX design, the more pages visited, the longer visitors stay on the site, and a greater increase in conversions can all be considered unambiguous triumphs.
On the other side, it's obvious that you need to improve UX design even more if you're not satisfied with your outcomes. Testing becomes important in this situation. Examine how users are interacting with your website, then run A/B testing and other crucial experiments to see which components could enhance your UX design. This can all be done in real-time, giving you a precise picture of UX as it develops.
When it comes to UX design, the more pages visited, the longer visitors stay on the site, and a greater increase in conversions can all be considered unambiguous triumphs.
UX design examples
1. Airbnb’s Booking Experience
In terms of developing a booking experience for websites that work, Airbnb is a UX design example that most people are familiar with. It's obvious that Airbnb did its homework. The homepage's layout addresses common problems that people encounter when looking for lodging.
The portal also provides information on famous neighboring destinations to help travelers who are unsure about where to go. It offers a variety of accommodations, including whole homes, pet-friendly homes, and special places to stay. Booking is an easy process that appears above the fold. Quick, easy to use, and clear.
2. Netflix
There are two Netflix's autoplay features that people have a love/hate relationship with.
- The Netflix ‘play next episode’ feature has made our minds up for us on more than one occasion. It’s a fantastic example of doing a job the user wants to do without even needing to ask.
- Netflix also introduced an autoplay trailer feature as you scroll through their media library—giving users quick insights into the movies and series they hover over. This particular autoplay feature was met with a great deal of controversy and debate.
3. Spotify’s Year Wrapped
Your social media feeds are probably flooded with end-of-year wrapped stories from Spotify. When it comes to the power of data and what it can do for your content, Spotify ranks as one of the best UX design examples.
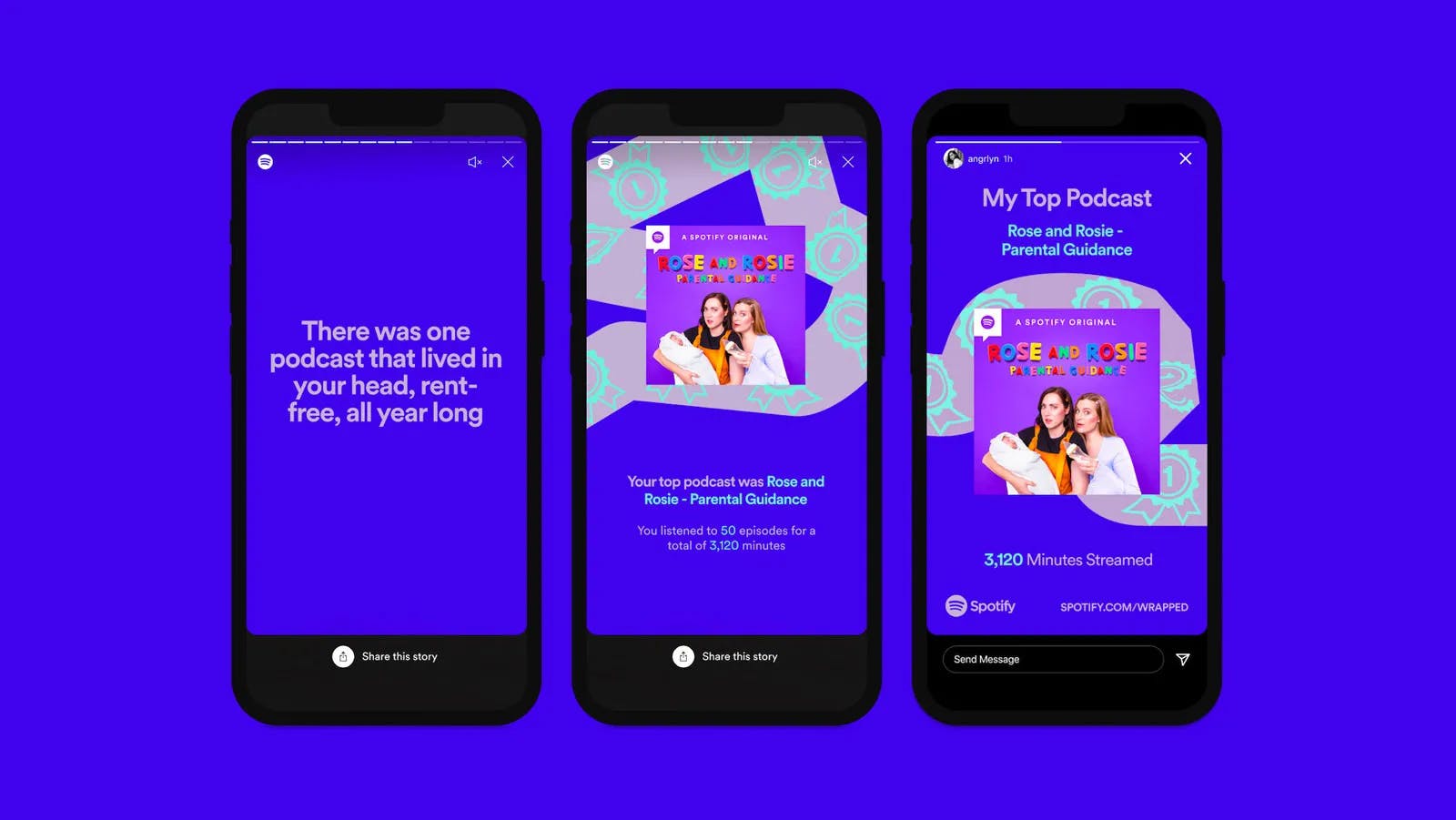
Spotify’s Year Wrapped.
They provide this content in a story format, which most people are accustomed to owing to Instagram, and give users the ability to share their tales with others in just one click.
Spotify takes the top spot on this list of UX design examples because of its creative data utilization, adherence to well-known conventions, and creation of an experience with the potential and simplicity to go viral.
UI & UX as Product Optimization
In your business category, customers have hundreds, maybe even thousands, of options. As a result of using sophisticated websites or programs throughout the years, they have also acquired refined tastes. They may have a propensity to look for alternative business solutions that can offer a better experience or a more intuitive interface when they discover a small business website and applications that fall short of their expectations.
Through UI optimization, fewer people experience problems as a result of confusion or errors. UX optimization is concerned with how much fun a user may have overall when browsing a website. These kinds of negative encounters can be avoided using UI and UX optimization services.
UI/UX Optimization's Business Benefits
- Reduces the risk of penalties in search engine rankings caused by various factors.
- Offers satisfying experiences to encourage visitors to stay longer and are more likely to return.
- Improves the quality of your company from the competition.
- Ensures that your website is simple to use and promotes conversions.
- Includes your branding throughout your website's design, user interface, and general atmosphere.
- Enhancing website functions including contact forms, eCommerce, social media integration, and customer care.

